Holla,
I’m currently attending Malaysia’s 2nd System Center Boot Camp 2012! So I got myself some hardware to play around and this post is a lil long, but I’ll be sharing some steps + screenshots on how you can configure a HAVMM(Highly Available Virtual Machine Manager). The guide here is purely for testing purposes and is not meant for Production!
For this environment we have the following Config:
- VM: PCloud.Local (Active Directory Server 2012)
- VM: VMMSQL01 (SQL Server 2012)
- VM: VMM01 (SCVMM Server 2012)
- VM: VMM02 (SCVMM Server 2012)
Installing SQL Server

Fire Up SQL Setup & Select Installation

Select “New SQL Server stand-alone installation or add features to an existing installation”
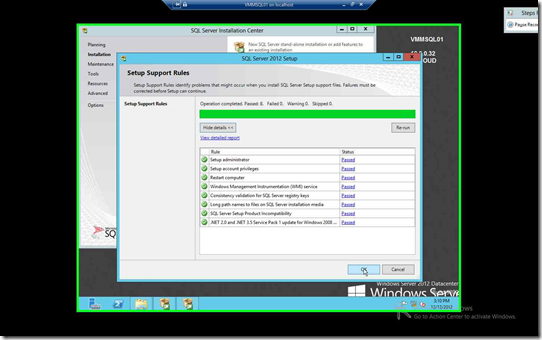
Allow the Setup Support Rules to finish its course and click OK
 |
 |
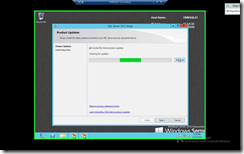
| You can skip the scanning for Product Updates if you chooses, but if you have Internet Connection, you should allow it to run. |
Click on Install & allow it to run its course. |
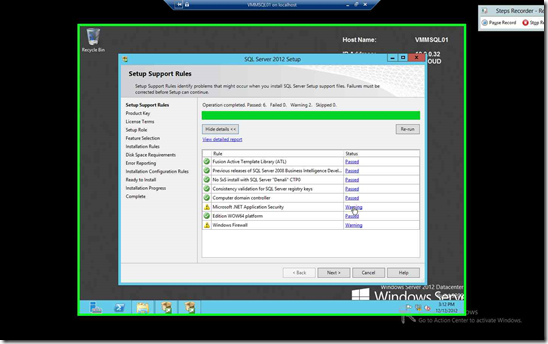
After the previous screen, the Setup Support Rules will run again, click next when it completes
 |
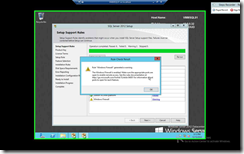 |
| Warning shows that the server cannot access internet hence there will be delay in starting .Net App. We can ignore this. |
Warning shows that we should allow appropriate Ports Open (This is important) |
Read through & Accept the license terms & click Next

After you’ve agreed to the license term & clicked next, you should select “SQL Server Feature Installation” & Click Next
 |
 |
| Select Database Engine Services |
Select Management Tools – Basic & Complete |

Once you’ve click Next after your roles selections, It will run another check. Click Next once it’s completed
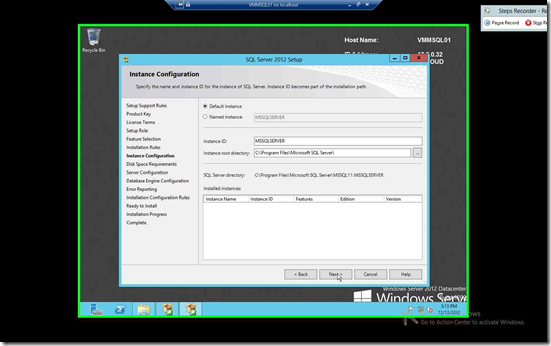
I’d leave it default to make things easier for me, Click Next Twice

I’d leave it as default as well & Click Next

Click on “Add Current User” & Click on “Add” your “SCVMMADMIN” user
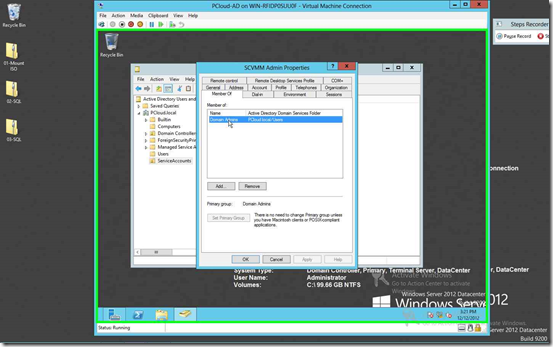
Point to note, SCVMMADMIN is also a member of Domain Admin

On Error Reporting Page Click Next and allow the Installation Configuration Rules to complete its check and click Next
 |
 |
| Click Install! |
Click Close & WahLah, you’re done, Only for SQL portion =’) |
Installing FailOver Cluster

Click on VMM01 and Add Roles & Features
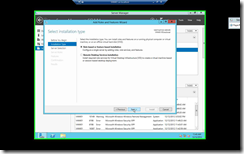 |
 |
| Select Role-Based or Feature-Based Installation & Click Next |
Select your preferred Server & Click Next |
 |
 |
| Click Next to get to Features |
Select Failover Clustering |
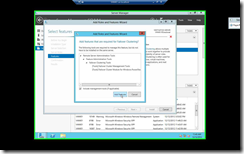 |
 |
| Add all additional Features |
Click Install |
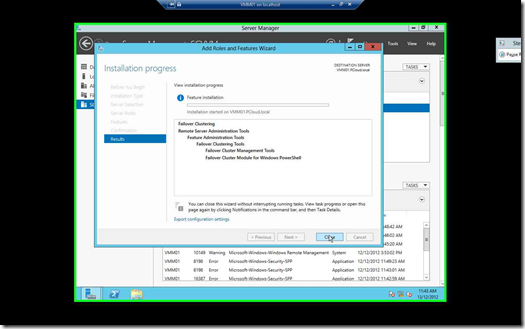
Click Close & Repeat the process but This time around, Install it on VMM02

Once both servers has complete it’s Feature Installation, Fire up the FailOver Cluster Manager & Click on “Create Cluster”

Click on Browse

Select Both of your VMM Servers! In this case it should be VMM01 & VMM02
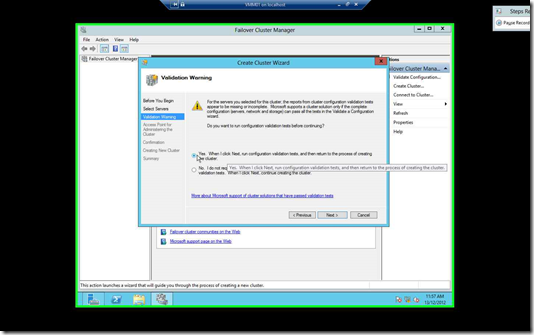
Once you click Next after the server validation, you will be prompted to run a Cluster Configuration Validation. Select “Yes” & Click Next

Select Run all test & Click Next. Follow the wizard and finish the Cluster Configuration!
Installing Highly Available Virtual Machine Manager

Fire up the SCVMM Setup file & Click on “Install”
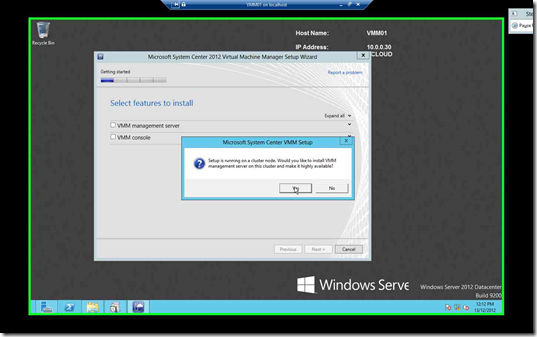
Setup detects that the Server you are installing is a HAVMM, click Yes & Proceed

Select “VMM Management Server“ & the VMM Console will be automatically selected. Click Next
 |
 |
| Key in something meaningful for you & leave the product key blank |
Accept the Term & Click Next |
 |
 |
| Click Yes @ the CEIP Screen |
Select On to Use Microsoft Update & Click Next |
For this particular installation, I’ve hit an interesting Error Message.
 |
 |
| VMM requires Deployment Tools & WinPE Features |
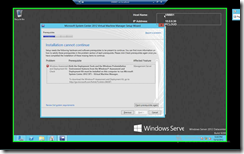
Fire up ADK Setup & Select “Deployment Tools”
“Windows PE” |
 |
 |
| Re-Run the Prerequisite Checks again & Click Next |
Provide the Server Name & Proper Credentials (SCVMMADMIN) & Click Next |
Here’ I stumbled again to another problem. I’m using SQL Server 2012 btw.
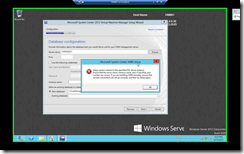 |
 |
| Warning says that it cannot find my SQL Server!!!! |
Looks like I’ll need to install 2 other add-ons! |
Fire Up “SQL Native Client” & “SQL Server 2012 Command Line Utilities” and follow the wizard.
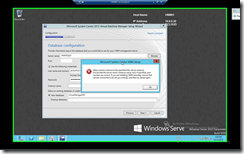 |
 |
| Well, I click next & I Hit the same error message again. This time around… It’s the Firewall in SQL Server |
Head over to SQL server & Turn Off all Windows Firewall *This is not for Production*
Head back & Click Next |
 |
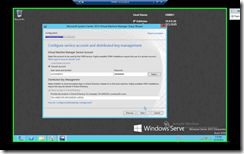 |
| Provide a meaningful name “HAVMM” & Provide a IP Address “10.0.0.35” |
Provide the proper Username & Password with a proper Distributed Key Management |
Click Next for the next 3 Screens & Complete the Installation by Clicking on Install Button
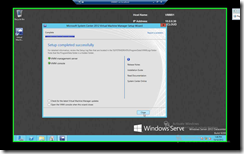
Click Close & Repeat the installation process to VMM02 & remember about the Prerequisites so that you don’t hit the same problem
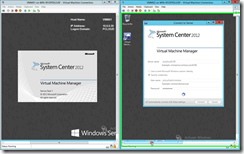
Fire up SCVMM on both VMM Servers and you will get an error message.
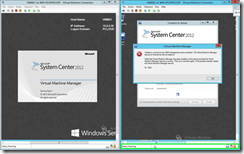
Turn Off the VMM Server which DO NOT have the Error Message.
That’s it, After this, you can install the VMM Console on any machine & you will be able to experience HAVMM =’)
Signing Off
K



















































